Imagine this: You’re on a crucial business trip, about to close a major deal. Suddenly, you find your laptop has been stolen, and with it, all your vital client emails, meeting notes, contract drafts, doodles on paint and a few (email) love letters you never managed to send to your crush.
A nightmare scenario, right?
This very real possibility highlights the critical importance of choosing the right email protocol for your business and even your email account. A dependable email system isn’t just about convenience. It’s also about data security, business continuity, and ensuring you can access urgent information when and where you need it.
What we’ll concentrate on are the two primary email retrieval protocols known as IMAP and POP3. We’ll dissect their functionalities, compare their strengths and weaknesses, and ultimately help you determine which protocol is the best fit for your business needs. For added peace of mind, we’ll even walk you through alternatives like EasyHosting.
- What Is IMAP?
- What Is POP3?
- IMAP vs. POP3: A Detailed Comparison
- What Is SMTP, Then?
- Choosing the Right Email Protocol for Your Business
What Is IMAP?
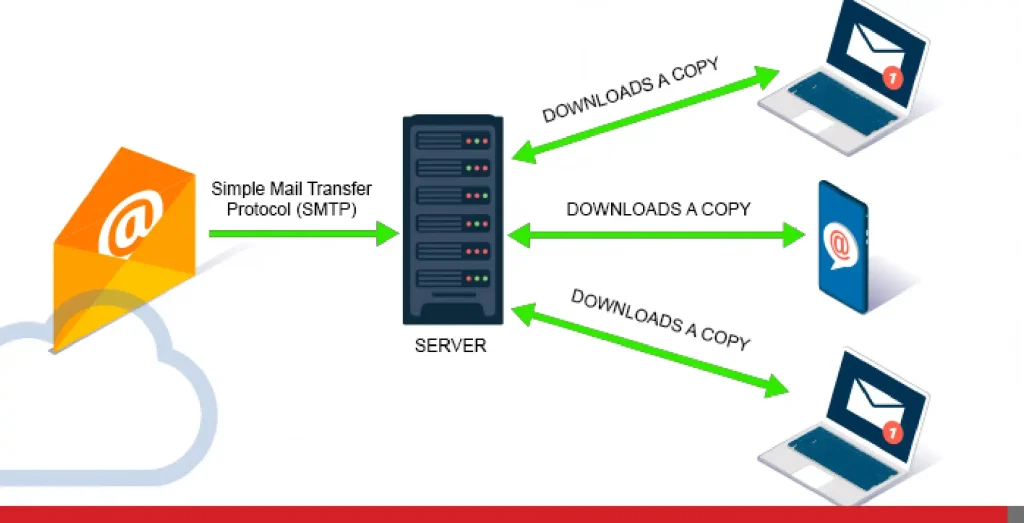
IMAP, or Internet Message Access Protocol, is the modern, sophisticated approach to email retrieval. Think of it as your email cloud. A cloud that will endure even after your stolen laptop embraces its new life!
Instead of downloading emails directly to your device, IMAP securely stores them on your email server. This means you can access your inbox from any device connected to the Internet—your office desktop, mobile devices, your tablet, or even a public computer in a library.
IMAP acts like a window into your email server, allowing you to view, organize, and manage your email messages instantaneously, no matter where you are.
A great email hosting account is essential for any business, whether it’s just starting out or if you’re ready to make the next step in growing your company. In all cases, EasyHosting’s robust and professional email solutions are ideally suited for businesses, small groups, or even freelancers and individuals who want to add a custom domain to their email.
How an IMAP Email Server Works
IMAP functions as a two-way communication channel between your email client (like Microsoft Outlook, Mozilla Thunderbird or the Apple Mail app) and your email server. When you open your email client, it connects to the server and synchronizes your inbox.
You see a mirror image of what’s on the server. Any changes you make—marking an email as read, moving it to a folder, or deleting it—are instantly reflected on the server and across all your other devices.
This real-time synchronization is a game-changer for productivity and collaboration.
Why IMAP Is Great for Business: Main Benefits
- Seamless accessibility: Access your email from anywhere with an Internet connection. No more being tied to a single device to get your new messages.
- Real-time synchronization: IMAP synchronizes emails across all your devices. Changes made in one place are instantly reflected everywhere.
- Enhanced collaboration: Multiple team members can access a shared mailbox simultaneously, improving teamwork and communication.
- Strong data security (with proper setup): Emails are stored on the server, offering a layer of protection against device loss or damage (assuming your provider has backups).
- Efficient storage space management: You can choose to keep all emails on the server, freeing up space on your local devices.
What Is POP3?
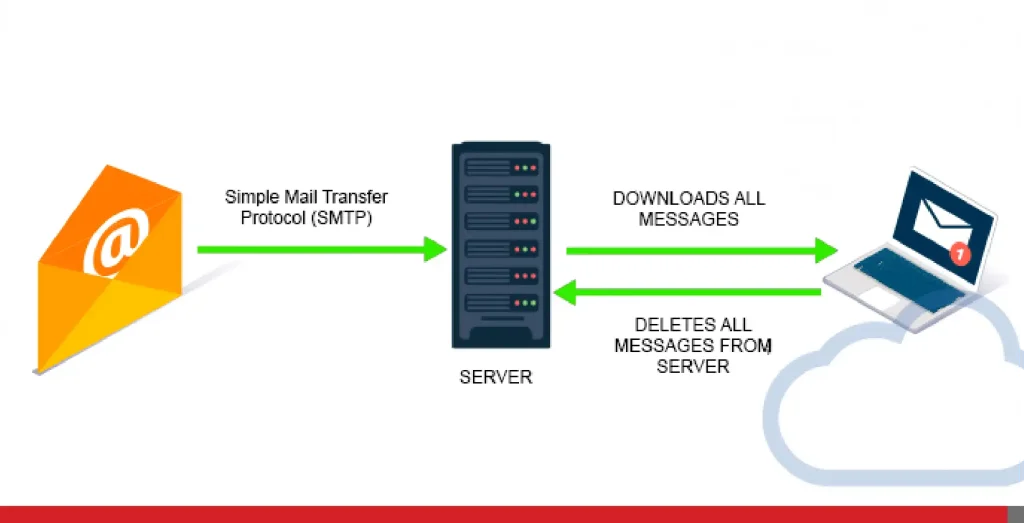
POP3, or Post Office Protocol version 3, is the older, more traditional method of retrieving email. Imagine it like a physical post office but without its people! When you use POP3, your email client connects to the server and downloads all new email messages to your local computer or local server.
Think of it like picking up your mail from a post office box. Once the emails are downloaded, they are typically deleted from the server (though this can be configured differently).
In the old days, you had to log in to the remote server, get your email and continue working from your desktop. And that was considered fast.
How a POP3 Mail Server Works
POP3 is a one-way street. Your email client retrieves the emails, and that’s often the end of the interaction with the server. The emails are now on your device, and unless you have separate backups, they are solely dependent on that device.
The stolen laptop from our example at the beginning that used POP3 would store all your email messages locally. So, if you didn’t have any recent backups, your data is lost (and so is your laptop, in case you didn’t notice).
Key Benefits of POP3 (Limited for Most Businesses)
- Offline access: You can read downloaded emails even without an Internet connection. This is the primary remaining advantage of POP3. However, you need an Internet connection in order to reply to a message. To some extent, offline access is also available in IMAP since most email clients use caching to store emails locally.
Key Drawbacks of POP3 for Business
- Single device limitation: POP3 is best suited for accessing email from only one device. Syncing across multiple devices is complex, and there is no native support.
- Synchronization nightmares: Emails are not synced across devices with POP3. Changes made on one device are not reflected elsewhere.
- Significant risk of data loss: If your device is lost, stolen, or damaged, you risk losing all your emails.
- Collaboration challenges: Shared mailboxes are difficult to manage with POP3.
IMAP vs. POP3: A Detailed Comparison
| Feature | IMAP | POP3 |
| Email Storage Space | On server | On local system |
| Access | Multiple devices, simultaneous access | Single device (primarily) |
| Synchronization | Yes | No |
| Data Backup | Server-side (provider dependent) | Local device (user responsibility) |
| Offline Access | Limited offline mode (can be configured) | Yes |
| Collaboration | Easy | Difficult |
| Security | Relies on SSL/TLS and strong auth | Relies on device security |
| Best For | Multiple device users, collaboration | Single device users, limited access |
IMAP Security Considerations:
- SSL/TLS encryption: Absolutely a must for secure IMAP communication. Ensure your email client and server are configured to use SSL/TLS.
- Strong passwords: Use complex, unique passwords for your IMAP accounts.
- Two-factor authentication (2FA): Enable 2FA whenever possible. This adds an extra layer of security, making it much harder for unauthorized access.
- Phishing awareness: Be vigilant against phishing attacks or malicious attachments. Never click on suspicious links or provide your email credentials to untrusted sources.
- Regular updates: Keep your email client and server software up to date with the latest security patches.
IMAP Limitations:
- Storage limits: Email storage is subject to the limits of your email provider’s plan.
- Server dependence: IMAP relies on the availability and performance of the email server. If the server is down, you can’t access your email. Although, some email clients cache past emails for you.

What Is SMTP, Then?
You could question some of your decisions, especially when you left your laptop unattended for a short break to get that juicy muffin at your local cafe. Now that you know all about the ancient POP3 and the modern IMAP email protocols, you may be curious about SMTP and its role in this blog.
Well, let’s explore the world of SMTP or Simple Mail Transfer Protocol. Think of SMTP as the trusty postal service of the Internet but without the cute mail trucks or the occasional dog chase. It’s the protocol responsible for sending emails from your email client to the recipient’s email server.
When you hit send on that email to your boss explaining why you’re late (again), the SMTP server takes over. It picks up your email message, wraps it up nicely, and sends it on its merry way to the recipient’s email server. From there, the recipient’s email client retrieves it using either IMAP or POP3.
An SMTP server often works with ports like 25, 465, or 587, depending on whether you’re using encryption (which you should, to keep those love letters safe from prying eyes).
So, next time you send an email, give a little nod of appreciation to SMTP, the behind-the-scenes system that makes sure your messages get delivered smoothly and securely.

Choosing the Right Email Protocol for Your Business
For the vast majority of businesses, IMAP is the clear winner. Its flexibility, accessibility, instant synchronization, and support for collaboration make it the ideal choice for today’s dynamic work environments. Most email hosting providers support IMAP for that particular reason.
POP3 could be considered only in very specific cases, such as a single user with extremely limited Internet access who prioritizes offline access above all else. However, even in these situations, the risks associated with data loss make POP3 a less desirable choice.
IMAP ports and configuration
- Default ports: 143 (unsecured) and 993 (SSL/TLS, which is the encrypted port).
- Configuration: You’ll need the IMAP server address, your email address (username), and your email password. Your email provider will provide this information.
Best practices for using IMAP
- Use strong, unique passwords.
- Enable two-factor authentication.
- Access your email over secure networks.
- Keep your email client software updated.
- Be cautious of phishing attempts.
Troubleshooting common IMAP issues:
- Connection problems: Check whether you have a good Internet connection and ensure your email client settings are correct. This is particularly important if you’re in the process of setting up your email account.
- Incorrect settings: Double-check the IMAP server address, port, username, and password.
- Server issues: Contact your email provider to inquire about any server outages or problems.
- Password issues: If you’ve forgotten your password, use your email provider’s password recovery process.
Conclusion
Back in 1971, when the first email was sent by Ray Tomlinson, there was just one email address. Yes, Ray sent an email to himself.
As of now, there are more than 4.4 billion email accounts around the globe, translating to an average of 1.86 accounts per person. Additionally, it’s estimated that over 360 billion emails are sent each day, which is astonishing.
IMAP offers a powerful and flexible solution for managing your business email, providing the accessibility, synchronization, and collaboration features that modern businesses demand. While POP3 would have served its purpose in the past, its limitations make it unsuitable for most businesses today.
By understanding the nuances of IMAP and following best practices, you can ensure your business email is secure, orderly, and always available.
Need help getting a business email with IMAP?
Choose from our current email options on EasyHosting today to find the one that meets your needs. We can also pair your professional email with a robust website by using our Website Builder!
Call us: 1-888-390-1210

FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
Does Microsoft Outlook use POP3 or IMAP?
Outlook can be configured to use either POP3 or IMAP. However, IMAP is the recommended setting for most users, especially those who access their email from multiple clients.
What should I put as the IMAP server?
The IMAP server address is specific to your email provider. You’ll need to consult your provider’s documentation or support resources to find the correct server address. It’s often something like imap.yourdomain.com, imap.mailprovider.com, or mail.hostingprovider.com.
Is Gmail a POP3 or IMAP?
Gmail supports both POP3 and IMAP. However, IMAP is the default and recommended setting for Gmail accounts.
How do I switch from POP3 to IMAP in Microsoft Outlook?
Switching from POP3 to IMAP in Microsoft Outlook involves a few steps, which may vary slightly depending on the version of Outlook you are using. Here’s a general guide:
- Backup your emails: Before making any changes, ensure you back up your existing emails to avoid any data loss.
- Remove the POP3 account:
- Open Outlook and go to File.
- Select Account Settings and then Account Settings again from the dropdown.
- Choose the POP3 account you wish to change and click Remove.
- Add the IMAP account:
- Go back to File and select Add Account. (Options could change on different Outlook versions.)
- Enter your email address and click Connect.
- Choose IMAP as your account type.
- Enter the incoming and outgoing server details provided by your email provider (it will be something like imap.mailprovider.com for IMAP and smtp.mailprovider.com for SMTP).
- Enter your email address and password when prompted.
- Configure settings:
- Ensure that the incoming server port is set to 993 with SSL/TLS encryption and the outgoing server port is set to 587 with STARTTLS encryption.
- Click Next and Finish to complete the setup.
- Test your account:
- Send a test email to ensure everything is working correctly.
By following these steps, you can successfully switch from POP3 to IMAP in Microsoft Outlook, allowing you to access your emails across multiple devices with instantaneous synchronization.